
VOC rotary concentrators
DEC.RBC™
Need to clean large amounts of air with low levels of solvents? A VOC Rotary Concentrator (DEC.RBC™) can help!
The rotor concentrator is an auxiliary air pollution control device that works alongside the main VOC treatment system, such as a solvent recovery unit or a thermal oxidizer. Imagine it as a pre-cleaner attached upstream before the main VOC abatement system. The concentrator traps the solvents (VOCs) from large solvent laden air (SLA) stream and squeezes them into a smaller, more concentrated stream. This concentrated stream then goes to the main VOC emission control plant, which can be a smaller unit because it has less work to do. The result? Up to 50% savings on utilities compared to using just an the VOC abatement system by itself!
DEC.RBC™ (VOC rotary bed concentrator) is used to remove volatile organic compounds (VOCs) low concentrated air streams: RBCs work by passing the contaminated air stream through a rotating bed of adsorbent material (DEC.HCA™ • Honeycomb Coated Adsorbent), such as zeolite or activated carbon. The VOCs are adsorbed onto the adsorbent, and the clean air stream is then exhausted to the atmosphere through a stack (FGS).
This process is ideal for treating large volumes of air, with small concentration of solvents (typically 0,1÷1,0 g/Nm3), typical application is the reduction of fugitive emissions (often due to equipment leaks and evaporative processes).

DEC.RBC™ • how it works?
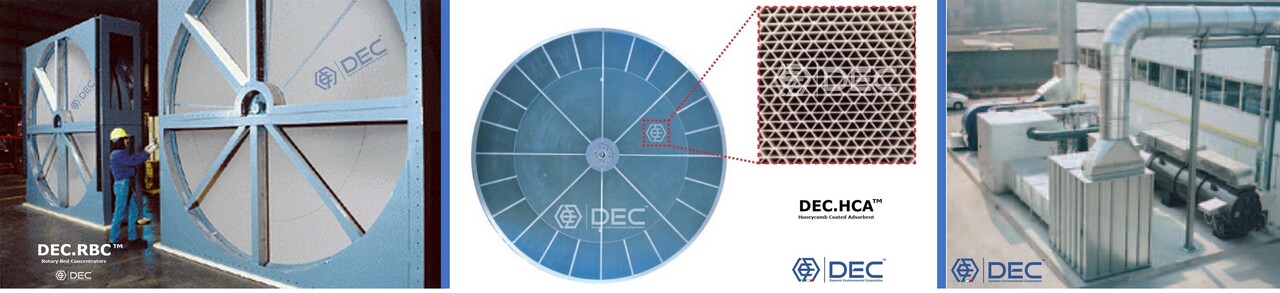
The heart of the DEC.RBC™ unit is a rotating ceramic honeycomb wheel filled with an adsorbent (DEC.HCA™ Honeycomb Coated Adsorbent).
The Solvent Laden Air (SLA) passing through the slowly rotating wheel (1÷3 rph), comes into contact with the absorbent bed (~80% of exposed surface), where the VOC are retained. During the rotation, the wheel passes through a regeneration section where hot air desorbs and concentrates the VOC in a flow stream smaller than the original SLA stream.
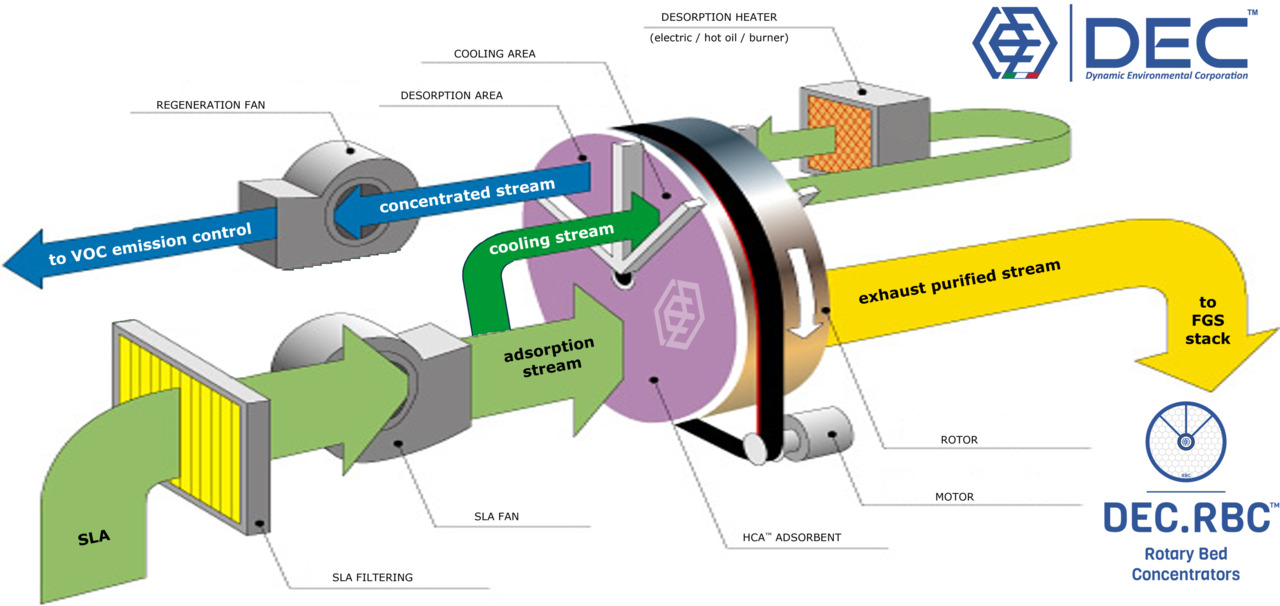
The RBC wheel is divided into adsorption, desorption, and cooling zones (typically 8:1:1 ratio). The adsorption is typically handled at 20÷35°C. Desorption through the regeneration (heated) air (at 180÷220°C), while the cooling zone aimed to cool down the DEC.HCA™ Honeycomb Coated Adsorbent to 50°C (or lower) so as to facilitate VOCs adsorption, once back to adsorption phase.
Once concentrated (typically <15 g/Nm3), the SLA can be efficiently treated in a VOC treatment system.
In this way the DEC.RBC™ unit reduces the volume of the SLA of 5÷8 times and concentrates the VOC in the same ratio.

DEC.RBC™ • benefits
The use of DEC.RBC™ rotary bed concentrators offers several benefits for industrial applications:
DEC.RBC™ • available sizes
The DEC.RBC™ unit is built in different diameters, from 1 ÷ 6 meters. Depending on the diameter, these units are provided pre-assembled (DEC.SMS™ - Smart Modular Systems platform), with a capacity 8.000÷50.000m3/h each or partially assembled at the Customer premises with a capacity up to 120.000m3/h cad.).
The size of a zeolite rotor for VOCs purification is usually very large, with some diameters reaching 4 m or more: in this case, the rotor-type adsorber generally consists of a block of spliced fan-shaped honeycomb bodies.
The unit is modular: utilizing, in parallel, more pre-assembled units, it's possible to treat reasonably an air volume equal to ~240.000 m3/h or even more.
For larger applications, thanks to customized design (DEC.CBS™ - Custom Built System), DEC.RBC™ units are modularly assembled on-site, with a capacity ranging from 150.000 ÷ 1.500.000 m3/h.
NOTE: the DEC.RBC™ unit should not be considered as an alternative to LEL recirculation systems (DEC.LEL™).
